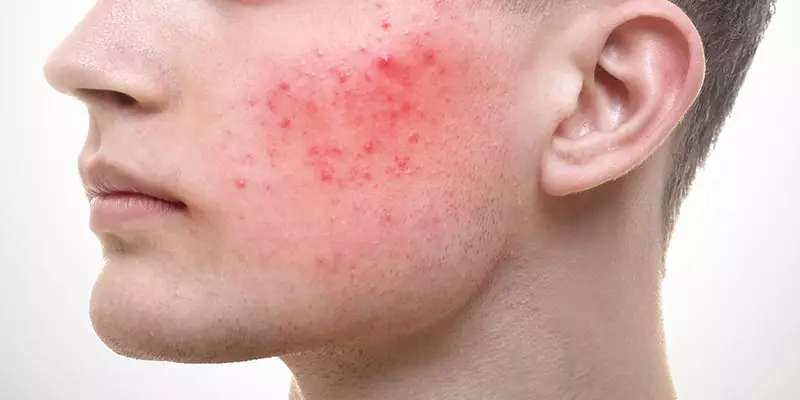
Rosacea is a chronic skin disease that most often affects the face like cheeks, nose, chin, forehead; common among fair-skinned people. The usual symptom is small, red, pus-filled bumps on the skin that are present during flare-ups. Flare-ups often occur in cycles; symptoms persist for weeks or months, disappear for some time, and then return.
Rosacea is also commonly known as Acne Rosacea
There are four subtypes of rosacea. Each subtype has its own set of symptoms.
Subtype 1: erythematotelangiectatic rosacea (ETR), characterized by flushing, facial redness, and thin visible blood vessels.
Subtype 2: papulopustular (or acne) rosacea, characterized by acne-like breakouts, and often affects middle-aged women.
Subtype 3: phymatous (rhinophyma) rosacea, is a rare form associated with the thickening of the skin on of the nose. It usually affects men and is often accompanied by another subtype of rosacea.
Subtype 4: ocular rosacea and its symptoms are centered on the eye area.
It is possible to have more than one subtype of rosacea at a time. The commonly noticed symptoms or skin changes in rosacea are:
Rosacea in most cases has classical presentation and in some atypical presentation need to be differentiated from the following conditions:acne vulgaris,seborrheic dermatitis, allergic or contact dermatitis,eczema or perioral dermatitis,auto-immune disease such as systemic lupus erythematosus, dermatomyositis,carcinoid syndrome,Demodex folliculitis,a bacterial infection caused by staphylococcus.
Rosacea recently has been found in association with certain auto-inflammatory diseases, including diabetes, inflammatory bowel disease, and cardiovascular disease
Causes: The exact cause is still not known, but it is more common among fair-skinned people. It can be due to hereditary and environmental factors. The overall changes seem to involve dilatation of the small blood vessels of the face.
It is not possible to prevent rosacea, but the preventive measures used by avoiding triggering factors will inhibit the flare-up of rosacea as mentioned below:
There is no specific medicine to rectify the problem. A combination of medications and lifestyle changes generally gives the best results. However, there are various treatments which can relieve the signs and symptoms
Topical medications: Topical antibiotics such as metronidazole and azelaic acid are commonly used preparation; even tretinoin, benzoyl peroxide, and sodium sulfacetamide can reduce inflammation and redness. Other topical antibiotics include erythromycin and clindamycin. Topical ivermectin 1% cream is also used. A very short-term mild topical steroids such as hydrocortisone 1% cream or desonide lotion can be used intermittently to reduce local inflammation. They are commonly used in combination with some oral medications.
Oral antibiotics: Oral antibiotics such as tetracycline, minocycline, and erythromycin; due to their anti-inflammatory properties tend to give faster results than topical ones. Doxycycline can be used in ocular rosacea to improve dryness, itching, blurred vision, and photosensitivity (sensitivity to light).
Isotretinoin: Isotretinoin can be used for severe cases of inflammatory rosacea if other treatment doesn’t work; as it a powerful inhibitor of sebum production, it should be used with caution.
Blephamide: Is a steroid eye drop can sometimes be used in ocular rosacea to relieve the eye symptoms.
Photodynamic therapy:Photodynamic therapy (PDT) uses a topical photosensitizer (aminolevulinic acid) liquid that one applies to the skin and light (blue light). PDT is newly used to rosacea and works by reducing the inflammation. PDT takes one to one and a half hours and strict sun avoidance for approximately one to three days is required after the treatment. It is advised to take with laser treatment to achieve the best results.
Light and Laser treatment:Commonly used are intense pulse light (IPL), long pulse Nd: Yag, and pulsed dye lasers. The treatment is safe, painless, but some may feel some discomfort, require multiple sessions for noticeable results, with an interval of 3-4 weeks. These lasers are used for vascular pathology responsible for rosacea which specifically targets visible blood vessels (telangiectasia). These lasers are used to shrink the blood vessels responsible for redness and will improve the skin and complexion. The gold standard among these lasers is a pulse dye laser.
Clear Skin Centre is the first laser center to have the most advanced pulse dye laser called Vbeam Prima.
