“Tinea” refers to skin infection with a fungus dermatophyte (ringworm)
Tinea is a fungal infection that causes a red and itchy circular rash in the moist areas of the human body, About 40 types of fungi can cause ringworm. It can infect any part of the body like the scalp, face, abdomen, groin, legs, fingers, etc.
Tinea is the name of a group of diseases caused by a fungus. These infections are usually not serious, but they are uncomfortable, itchy and contagious by touching an infected person or from damp surfaces such as shower floors, or even from a pet.
Depending on which part of the body is affected, it is given a specific name.
The name can sometimes convey a different meaning.
Pityriasis Versicolor is the correct medical term for Tinea versicolor. This is a common yeast infection on the trunk.Tinea incognita (often spelled incognito) refers to a tinea infection in which the clinical appearance has changed because of inappropriate treatment.Tinea nigra is a mould infection (not a dermatophyte). It affects the palms or soles, which appear brown (on white skin) or black (on dark skin).
If you are overweight, try to lose weight to reduce chafing and sweating(helpful in t.cruris)
Ringworm is difficult to prevent from spreading, as the fungus is so common and contagious even before symptoms appear. Take these steps to reduce your risk of ringworm:
In general for mild cases of tinea, topical antifungal agents may be sufficient, but oral antifungal is typically needed if the fungal infection includes a hair-bearing site, is severe, or has not cleared with topical antifungal.
Oral antifungals medicines include griseofulvin, fluconazole, terbinafine and itraconazole. Griseofulvin is effective for trichophyton infections and is less effective for microsporum species.
Topical agents such as povidone-iodine, clotrimazole or serticanazole or lulicanazole lotions are used.
Medicated shampoo containing ketoconazole or selunium sulfide helps to prevent the fungus from spreading in case of T.capitis
In case of tinea pedis general measures should be first-line, including meticulous drying of feet, especially between the toes, avoidance of occlusive footwear, and the use of barrier protection (sandals) in communal facilities. Patients with the hyperkeratotic variant of tinea pedis may benefit from the addition of a topical keratolytic cream containing salicylic acid or urea
Tinea unguium often takes several months to cure and it is more to return even after treatment. Light therapies and laser devices to treat Tinea Unguium include 308 excimers, targeted phototherapy and laser technologies like Nd-Yag lasers and diode lasers are developed to treat tinea unguium.Prednisone, if the lesions are severely inflamed (kerion), a short course of prednisone should be added to lessen the symptoms and reduce the chance of scarring.
Tinea barbae is a fungus that infects the hair. Tinea barbae is caused by a dermatophytic infection in men’s beards. In most cases, the infection manifests as a follicular inflammation or a cutaneous granulomatous lesion, i.e. a chronic inflammatory response. It’s one of the reasons for folliculitis. It is most common among agricultural workers because transmission from animals is more common.
The most common symptoms of tinea barbae are pimples or blisters in the affected area, swelling and redness around the infected area, and red and lumpy skin on the infected area.Crusting around hairs in the infected area will occur, and Hairs in the infected area will be easy to pull out. Tinea barbae can cause itching and pain when touched, but these symptoms do not always occur.
Treatment depends on the severity of the infection. Topical antifungal medications can be used to treat mild cases of tinea barbae. Topical antifungal medications are typically available in the form of cream, which can be purchased over the counter. More severe tinea barbae cases necessitate the use of an oral antifungal medication, oral antifungal medicines include Terbinafine and Itracanazole.
Tinea capitis is a fungal infection that affects both the skin and the hair on the scalp. Ringworm of the scalp is another name for it. Hair loss, dry scaly areas, redness, and itching are all symptoms of tinea capitis. Tinea barbae is a similar condition that affects the beard area.
Tinea capitis is associated with at least eight dermatophyte species. Dermatophytes from the genera Trichophyton and Microsporum infiltrate the hair shaft and cause the disease.
The clinical presentation is usually characterised by single or multiple patches of hair loss, sometimes with a ‘black dot’ pattern and frequently with broken-off hairs, which may be accompanied by inflammation, scaling, pustules, and itching.Tinea capitis is uncommon in adults, but it is more common in pre-pubertal children, particularly boys.
Thickened, scaly, and occasionally boggy swellings, as well as growing raised red rings, can be seen. Extreme scalp itching, dandruff, and bald patches where the fungus has entrenched itself in the skin are all common symptoms. It often presents identically to dandruff or seborrheic dermatitis.
House pets, such as cats and dogs, can spread tinea capitis, too. Farm animals like goats, cows, horses, and pigs can also be carriers. However, these animals might not show any signs of infection.
Because topical agents cannot penetrate the root of the hair follicle, tinea capitis always necessitates systemic treatment. Previously, griseofulvin was the most commonly used medication to treat tinea capitis. Newer antifungal agents such as terbinafine, itraconazole, and fluconazole are available now.
To minimise spore transmission, topical agents such as povidone-iodine, ketoconazole, and selenium sulphide shampoos may be used.In cases of zoophilic infection, family pets should be examined and handled by a veterinarian.
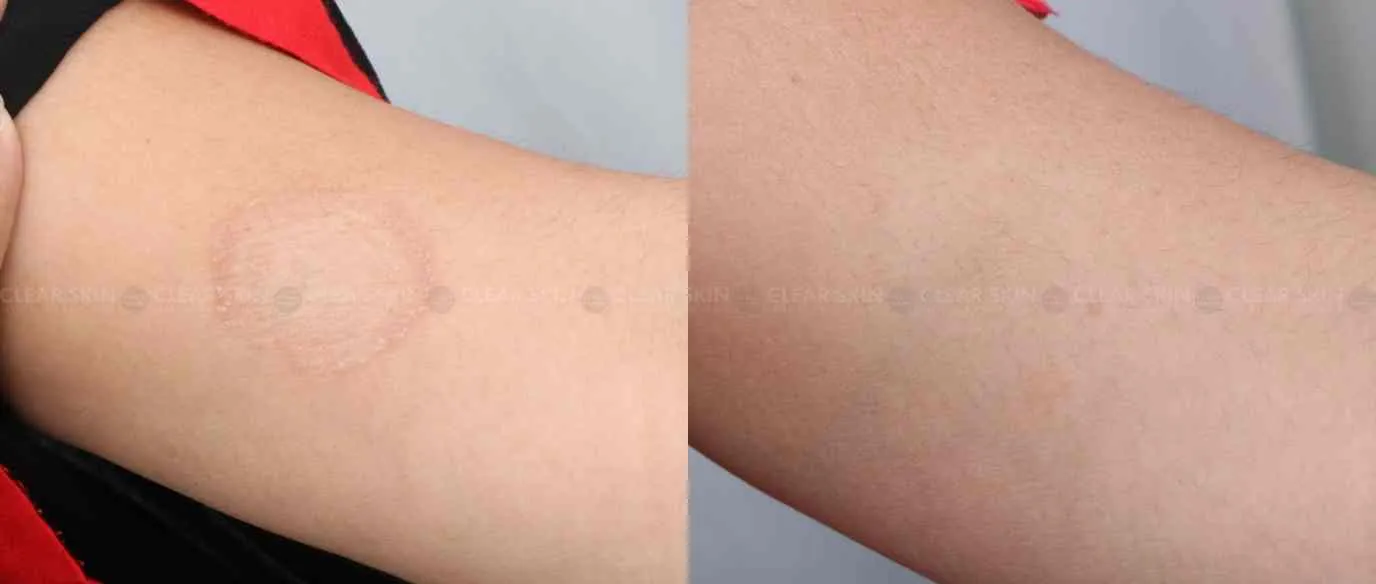
Tinea corporis is a skin infection caused by a fungal infection that can affect every part of the body except the hands and feet, scalp, face and beard, groin, and nails. With its distinctive ring-shaped lesions, it is generally referred to as ‘ringworm.’
Tinea corporis is transmitted by fungal spores shed from infected skin. A warm, moist climate, as well as the sharing of fomites likes bedding, towels, and clothes, aid transmission. The incubation period will last anywhere from 1 to 3 weeks. In healthy skin, the dermatophyte normally invades and spreads in the stratum corneum, but it cannot penetrate deeper layers.The itchy, scaly ring-shaped area, typically seen on the buttocks, trunk, arms and legs, slightly raised with expanding rings with scattered papules
The majority of cases are treated with topical antifungal creams applied to the skin, but in severe or difficult-to-treat cases, oral medication may be needed. Recommended oral agents are terbinafine and itraconazole.
General measures have to apply for good results, it’s important to keep your skin clean and dry. In hot, humid climates, loose-fitting light clothing is recommended. Stop getting into direct contact with infected people and exchanging fomites. The risk of re-infection is minimised by testing household members and pets for the source of infection and prescribing adequate care.
Tinea Cruris is the name given to a dermatophyte fungus infection of the groin. Adult men and women are the most commonly affected. Tinea cruris, or jock itch, is a popular ailment.The rash has a raised red scaly border that extends from the groin or scrotum down the inner thighs. On the buttocks, Tinea cruris can cause ring-like patterns. It is rarely seen on the penis, vulva, or around the anus, and it is very itchy.
Antifungal drugs are added to the groin area to treat tinea cruris. Terbinafine or itraconazole should be taken by mouth if the symptoms have been present for a long time or the condition has worsened through the use of creams.
Cotton underwear and socks, as well as keeping the groin dry and applying antifungal powders, are all beneficial.Concurrent fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot, must be managed to prevent tinea cruris recurrence. Keeping the groin area dry, avoiding tight clothes, and losing weight if obese are also recommended to prevent moisture build-up. Athletes foot or tinea cruris sufferers may avoid spreading the infection by not lending their towels to anyone.
Tinea faciei, also called tinea faciale or facial ringworm, is a fungus-caused infection of the skin on the face. The infection typically begins as a red or pink patch that becomes raised and itchy over time, with the middle of the patch resembling normal skin.
Tinea faciale is characterised by pink, ring-like, slightly raised lesions with scaling around the edges. It is most common in hot, humid climates.Ringworm infection on the face is most common in adolescents and young adults, as well as patients with compromised immune systems.
The majority of infections can be treated with antifungal creams. Oral antifungals can be used to treat infections that are more severe or have been present for a long time. Since using an appropriate drug, the ringworm should go away in 4–6 weeks.
Tinea manuum is a dermatophyte infection that affects one or both hands. Tinea manuum is a slightly less common form of tinea, and you can get it by rubbing your infected feet or groin. An anthropophilic (human) fungus is the most common cause.
On the palm of one hand, it usually manifests as a slowly expanding region of peeling, dryness, and slight itching. Skin blemishes can be emphasised. In most cases, both feet are affected and tend to be the same “one side, two-foot syndrome.”
These fungi may also cause a blistering rash on the tips of the fingers or on the palm of the hand. The blisters appear in the form of a sticky clear fluid and appear in crops. It’s likely that they have a peeling finish. Tinea manuum causes itching and burning.
Though anyone can get tinea manuum, but it is more likely to infect people with:
It can usually be treated with long-term use of a topical antifungal medications. However, in some cases an oral antifungal such as griseofulvin may have to be prescribed.
Tinea pedis is the most common dermatophyte infection, with T. interdigitale being more common than T. rubrum. It is more common in humid, tropical, urban environments.Tinea pedis is most common in males, teenagers, and young adults, but it can also affect women, infants, and the elderly. Oozing and ulceration between the toes (ulcerative type) or pustules are uncommon symptoms.
The conventional treatment includes thoroughly washing the feet once or twice a day, accompanied by the application of a topical drug. Since the outer skin layers have been weakened and are vulnerable to reinfection, topical therapy is usually continued until all layers of the skin have been replaced, which takes around 2–6 weeks after the symptoms have gone away.
Topical antifungal agents, which come in the form of a spray, powder, cream, or gel, may be used to treat the fungal infection.Oral terbinafine is more beneficial than griseofulvin for moderate or refractory cases of athlete’s foot. Fluconazole or itraconazole may also be taken orally for severe athlete’s foot infections.
Tinea unguium, also known as onychomycosis, is a fungal infection of the nails. It affects one or more toenails and fingernails, and most often involves the great toenail or the little toenail. It is more common in older age groups (men) and is rarely seen in adolescents.
It may affect one or more toenails and fingernails, and more often involves the great toenail or the little toenail. It’s more common in people with diabetes, psoriasis, peripheral vascular disease, or another immune-suppressing condition.It appear as brittle, thick, hard, discolored, yellow to brown or black, irregular in shape and texture. The nail may also have white or colored material under it. If left untreated, the fungus may spread to its nail bed and the nail may also fall off.
In most cases, fingernail infections heal faster and more easily than toenail infections.Mild infections affecting less than 50% of one or two nails may react to topical antifungal medications, but cure typically takes several months of taking an oral antifungal medication. Non-drug therapies for onychomycosis have been introduced in recent years, avoiding the side effects and complications associated with oral antifungal medications. Lasers that emit infrared radiation are thought to destroy fungi by creating heat inside infected tissue. With one to three almost painless sessions, laser therapy is said to safely remove nail fungi.
| DO | DON'T |
|---|---|
| Keep your skin dry at all times, especially after bathing and in between the toes | Don’t itch or rub the affected area as it makes the rash worse. |
| Keep your personal hygiene, take twice a bath, and preferably use lukewarm water | Do not share your personal items such as clothes, towel, soap, or comb with your family members or friends. |
| Wear only loose, airy cotton clothes | Don’t use nylon and synthetic clothes as much as possible |
| Use a towel or a tissue paper to pat dry areas with sweat | Do not forget to check your pet animals for rashes, as dogs and cats are also the sources of infection. |
| After gym or a workout session, take a shower and clean yourself thoroughly | Do not forget to keep your body weight ideal, as overweight or undernourished leads to reduced immunity. |
| Do ask your family members having similar infection, as they may become source for re-infection. | Don’t forget to check your blood sugar levels, if you are diabetic |
| Do change your socks whenever your feet feel damp. | Don’t: wear the same pair of shoes over and over |
| Do wear flip-flops or shower shoes in the gym locker room and while shower, at the nail salon and any other public place where people tend to walk barefoot. | Don’t: put off getting a suspected fungal infection evaluated by your dermatologist. |
| Do choose natural materials like leather and canvas and styles that allow air to circulate. | Don’t: wear shoes made of vinyl or plastic that does not allow feet to breathe. |
| Do complete the full course of medications prescribed by your dermatologist. | Do not incomplete the treatment, as it may results in recurrence of fungal infection which is more resistant to treatment. |
| Do avoid using home remedies such as garlic paste as it could burn your skin. | Do not use over-the-counter (OTC) medications for ringworm, as most they contain steroid. |